Different methods of measuring KPIs
Measuring KPIs can be done in both traditional and digital manner.
Traditional ways of measuring KPIs include measuring KPIs in excel or spreadsheets, paper-based reports, periodic performance reviews, and manual data entry from reports. These KPI analysis reports ended up being time-consuming and error prone, difficult to compare across teams, getting delayed insights hindering proactive action, and lack of visualising and real-time tracking.
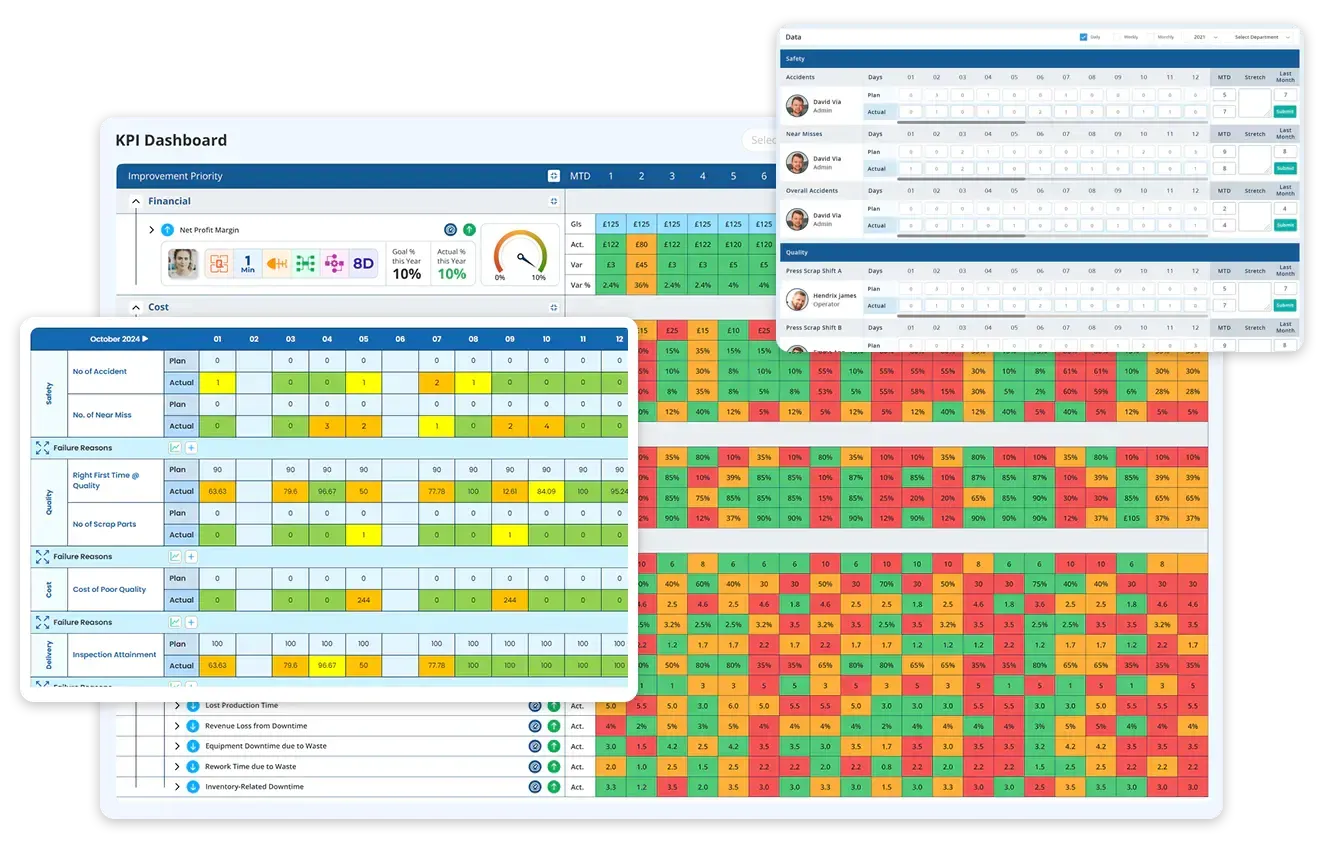
Digital tools for measuring KPIs made this much easier and more effective. Some of these include dashboard-based measurement (Balanced Scorecard), IoT and sensor integration, ERP/CRM integration, predictive KPI analysis, mobile and cloud KPI tracking, and automated reporting and alerts. Some of the advantages included real-time visibility, data accuracy and integrity, predictive insights, easy collaboration and transparency, and scalability across locations and teams. Digitally analysing KPIs would be the best KPI measurement method for managers.
Best practices for measuring KPIs
Measuring KPIs can be tricky, mainly because there are qualitative KPIs just as much as there are quantitative KPIs. To keep an eye on various KPIs, it is important to make them measurable for easy comprehension and strategic planning. It is also important to keep in mind that KPIs should measure performance and not the activity.
To streamline performance tracking and strategic alignment, businesses increasingly rely on tools for measuring KPIs such as digital dashboards, Balanced Scorecards, and ERP-integrated analytics platforms. These tools not only automate data collection but also provide real-time insights and visualisation, making KPI tracking more efficient and practical. For instance, a KPI measurement example in manufacturing could be tracking Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) using a formula that combines availability, performance, and quality. To simplify implementation, organisations can use a KPI measurement template that outlines key elements like KPI definition, calculation method, data source, owner, and review frequency—ensuring consistency and clarity across departments.
Understanding how to track KPIs are just as important as choosing them. Here are a few ways on how to track KPIs:
1. Define the KPI clearly: First thing to note before measuring KPIs is to be clear about what the KPI stand for.
What to include:
- What is being measured
- Why it matters
- How it will be calculated
- Who owns the KPI
- How often it will be monitored.
Example: Take the example of customer retention rate.
- What: Percentage of customers who stay over a period
- Why: Suggests customer loyalty and satisfaction
- Owner: Sales or customer success
- Frequency: Monthly
2. Set a baseline and target: The baseline will be current performance level which acts as the starting point and the target will be the desired performance level which is aligned with strategic goals. This helps measure progress and gap clearly.
Example:
- Baseline: 75% on-time delivery
- Target: 95% within 6 months
3. Use a reliable formula: Each KPI should have a standardised formula for consistency.
Example:
- Profit margin: (Net profit / Revenue) x 100
- Employee turnover rate: (Number of exits / Average headcount) x 100
- OEE: Availability x Performance x Quality
4. Collect accurate and consistent data: Collecting accurate and consistent data is a must to measure KPIs properly.
- Recognise data sources (CRM, ERP, HRMS, production logs, surveys, etc.)
- Ensure data quality (accuracy, timeliness, completeness)
- Automate data collection wherever possible to reduce manual errors
5. Determine the measurement frequency: The goal here is to balance timeliness (to act fast) with trend precision (to see patterns).
- Strategic KPIs: monthly or quarterly
- Operational KPIs: daily or weekly
6. Visualise and monitor over-time: Use dashboards, scorecards, or control charts to visualise KPI trends. Visualisation makes it easy to spot deviations and drive corrective actions.
How to avoid common mistakes when measuring KPIs?
Understanding how to choose appropriate KPIs and how to accurately measure them is only half the journey. The next step which may seem simple is one of the most important ones.
Let's see what the most common mistakes are every company makes when measuring KPIs.
- Measuring too many KPIs: Trying to monitor too many data leads to information overload and dilution of focus. Instead, it’s always better to focus on 3-7 meaningful KPIs per goal.
Example: Instead of tracking 25 manufacturing metrics, focus on OEE, defect rate, and delivery performance.
- Choosing irrelevant metrics: Irrelevant metrics or vanity metrics are those metrics that seem impressive but don’t drive real outcomes.
Example: Instead of tracking number of website visitors, it is better to track website conversion rate or leads generated per visit.
- No clear link to business goals: KPIs that aren’t tied to strategic goals don’t show whether the industry is moving forward or not. It's better to start from the organisational goals, then define KPIs that quantify progress toward them.
- Lack of clear definitions and formulas: If KPIs are not clearly defined, people interpret them differently.
Document: KPI definition, KPI formula, data source, frequency, and owner.
Example: Productivity could mean output/hour or output/employee.
- Inconsistent or unreliable data: This means data errors, manual entry mistakes, or unstandardised sources lead to misleading conclusions. Use automated systems and data validation wherever possible to guarantee accuracy and consistency.
- Ignoring leading indicators: Always relying on lagging KPIs is not enough. There should be a balance between leading and lagging KPIs.
- Not setting targets or benchmarks: Not setting targets will make judging success impossible. Define SMARTER targets – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound, Evaluate, Readjust.
- Not analysing or updating KPIs: KPIs begin to lose relevance as strategies and markets evolve. Keep an eye on KPIs periodically – drop outdated ones and add new ones aligned with current goals.
- Focusing only on quantitative data: As we have already seen before, there unmeasurable KPIs which are also important. Try to combine quantitative KPIs like defect rate with qualitative ones like employee feedback.
- Lack of clear communication and accountability: If employees don’t understand what KPIs mean or how they influence results, they won’t be able to act on them. Cascade KPIs clearly and assign ownership to drive engagement.
It's quite natural to make mistakes in the very beginning, but it’s better to avoid them as soon as possible.
Interested to know more on how to measure KPIs?