What does SQDCM stand for?
SQDCM stands for Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, and Morale. These are five daily performance areas tracked to improve operations and reduce waste.
What is a SQDCM Board?
An SQDCM Board shows key daily performance results in one place, helping teams in Lean and shop floor operations track Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, and Morale at all-in-one places. This operational performance board serves as a central communication hub for teams, providing real-time visibility into performance targets and progress. The board typically includes colour-coded indicators to track accident rates, defect counts, on-time delivery, production costs, and employee satisfaction. This visual management board facilitates continuous improvement efforts by fostering transparency, accountability, and collaboration among team members, ultimately driving operational excellence and productivity
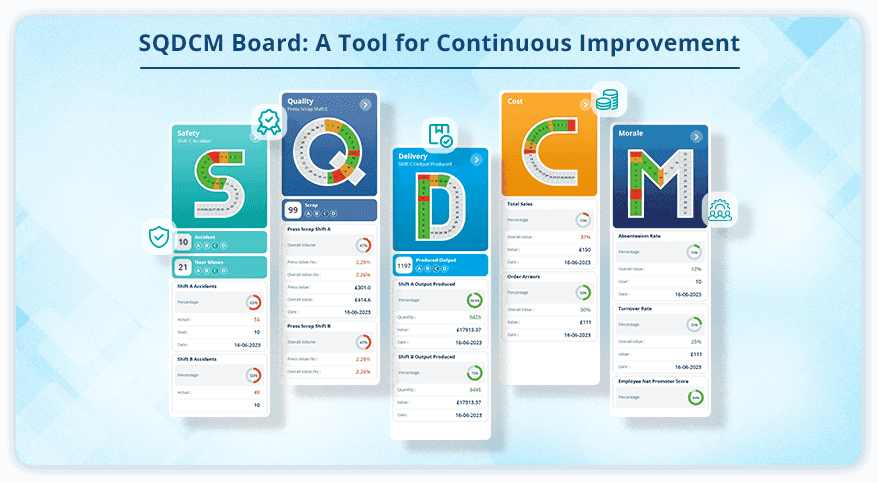
An example of SQDCM visual management dashboard or Diagram
Understanding SQDCM Metrics: Driving Continuous Improvement
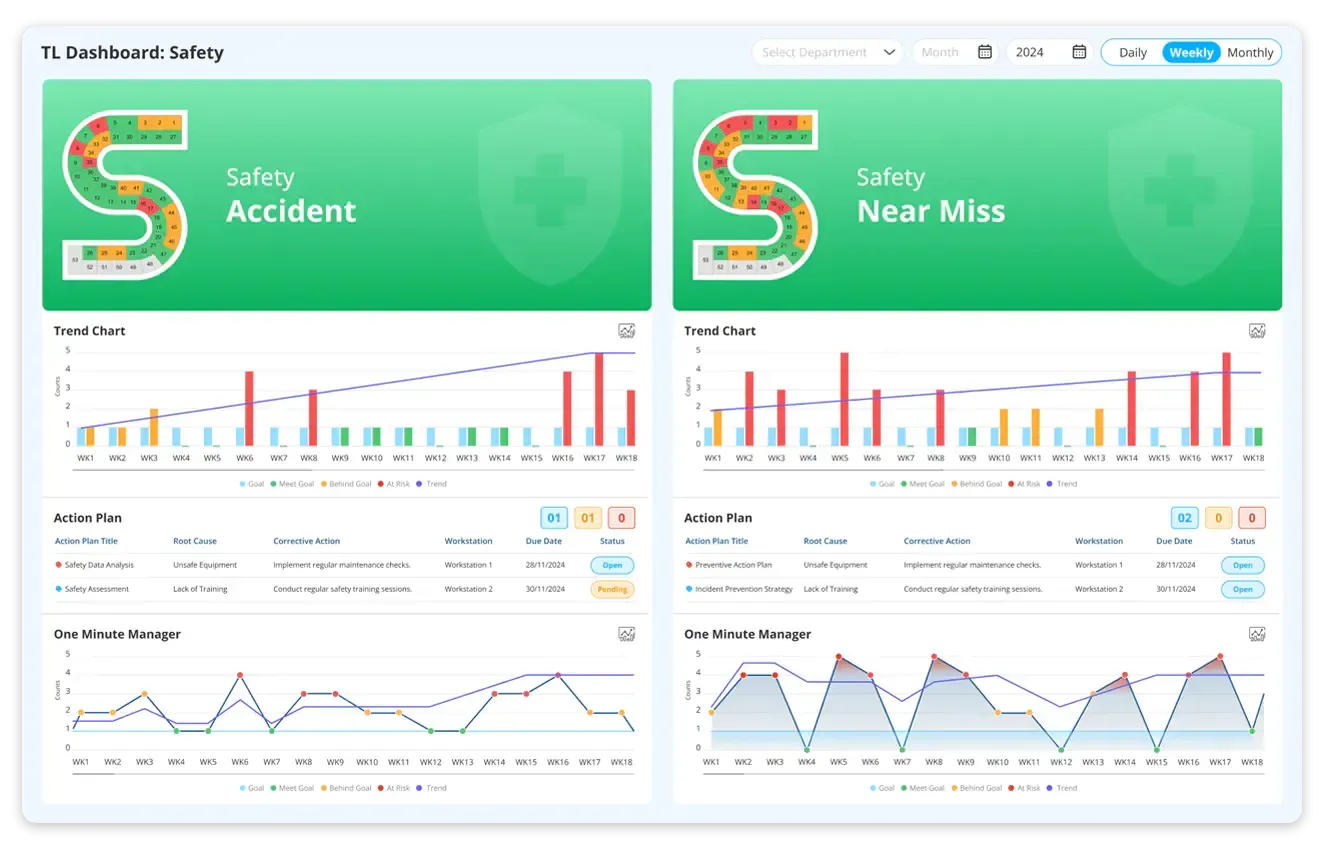
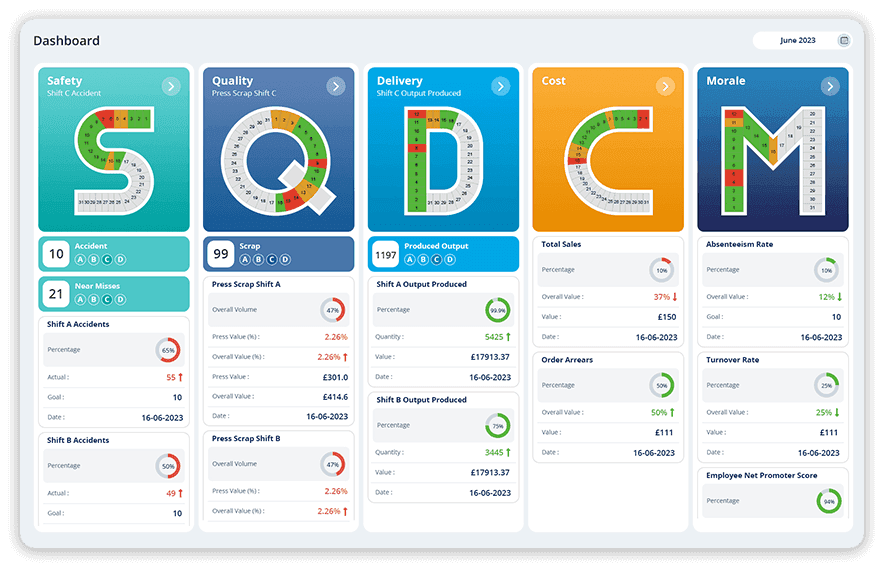
Safety: An SQDCM board can track safety to ensure a comprehensive approach to monitoring and improving workplace safety. Organisations can effectively analyse how the safety metrics perform to prioritise risk mitigation and drive continuous improvement initiatives.
Read How SQDCM Enhances Organisational Safety Goals? , for more insights.
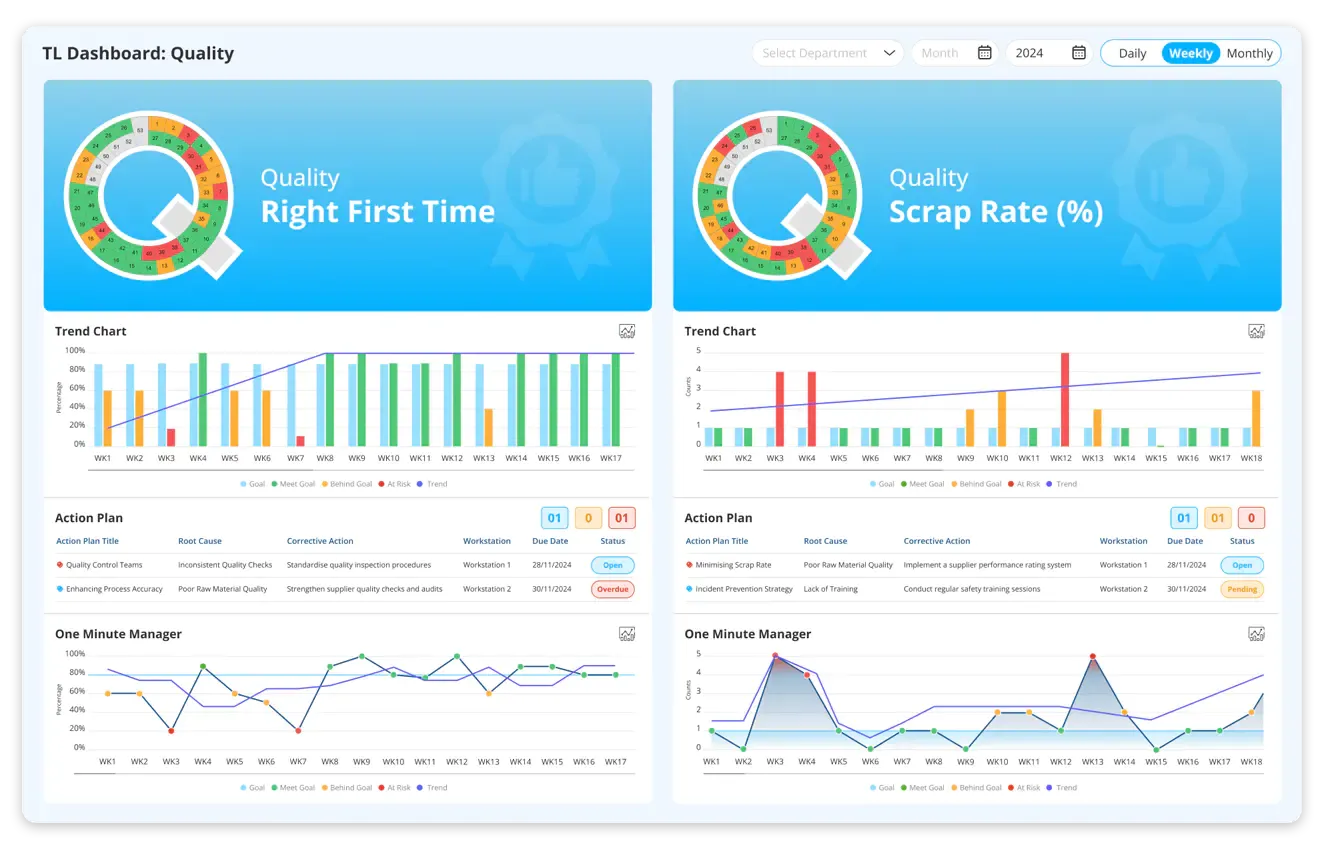
Quality: Manufacturers can use an SQDCM digital system to analyse quality metrics to gain insights into product quality, process efficiency and customer satisfaction. Tracking metrics like defect rates, customer complaints, and adherence to standards enhances the overall quality of processes.
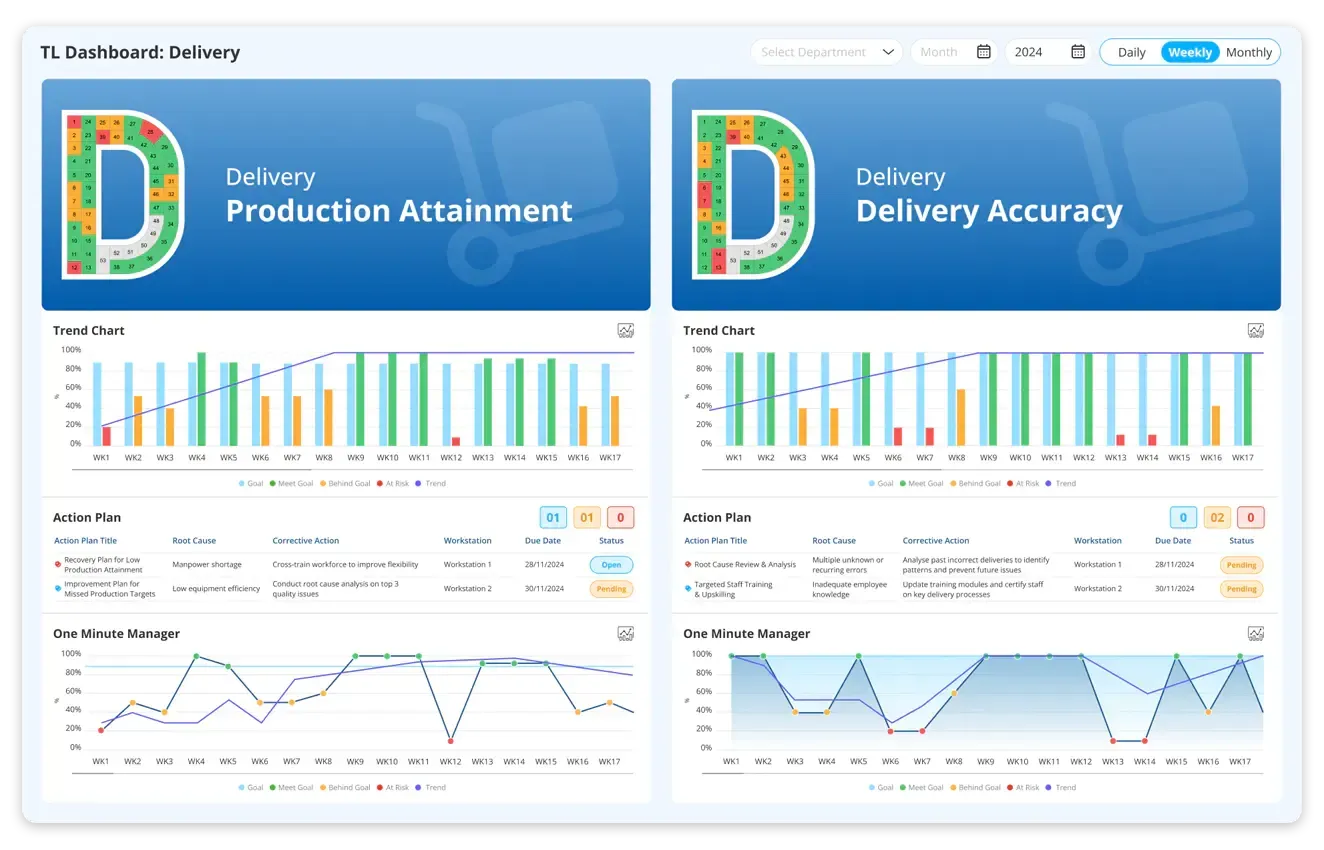
Delivery: Delivery metrics within the SQDCM visual management board comprehensively evaluate a manufacturer's supply chain efficiency and reliability. These metrics encompass on-time delivery, lead time, and order fulfilment, offering insights into the timeliness and effectiveness of delivering products to customers.
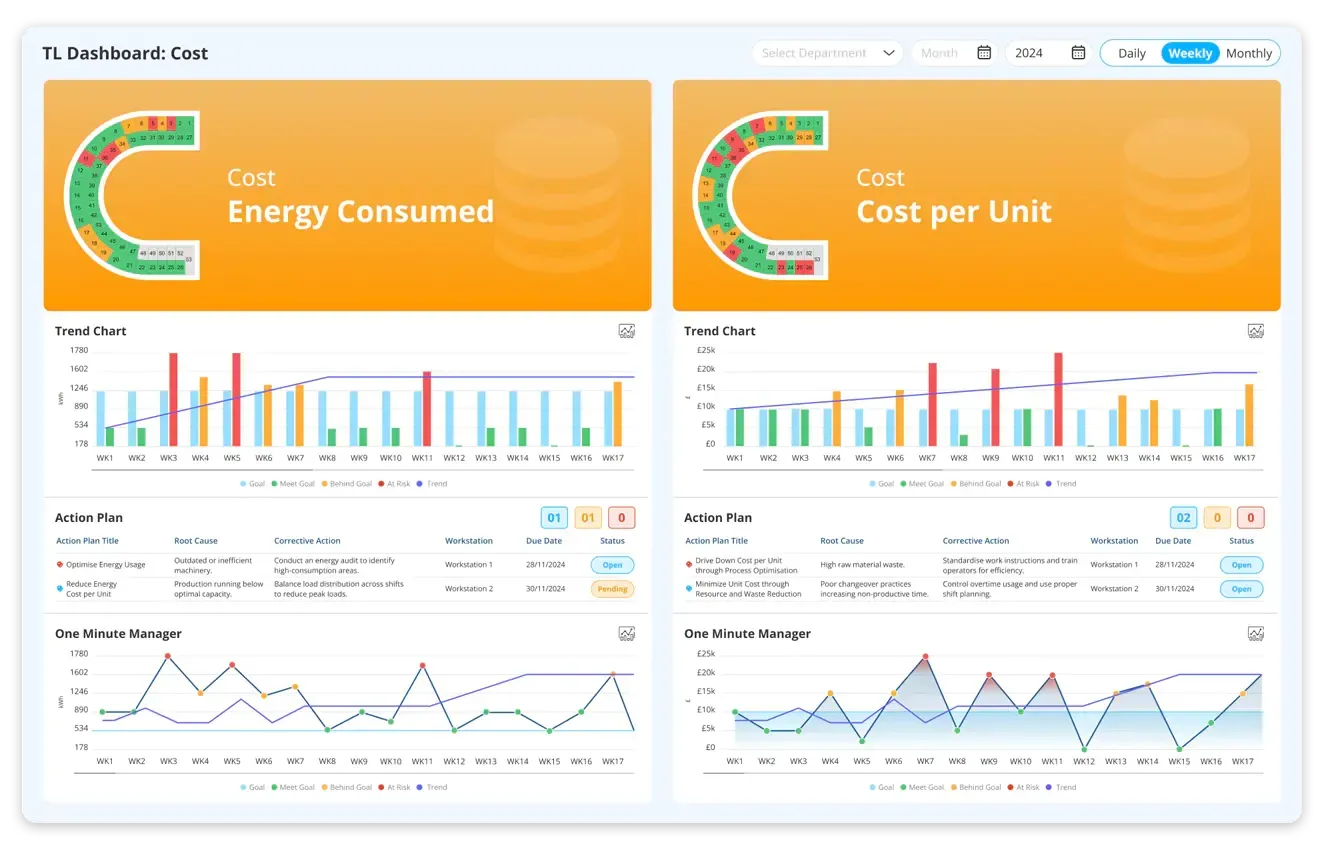
Cost: Cost is a key metric in the SQDCM huddle board used by organisations to align business activities with their vision and strategy. Cost as a metric in this perspective helps measure and manage the efficiency of business processes, control expenses, and optimise resource allocation. It allows organisations to ensure profitability and sustainability.
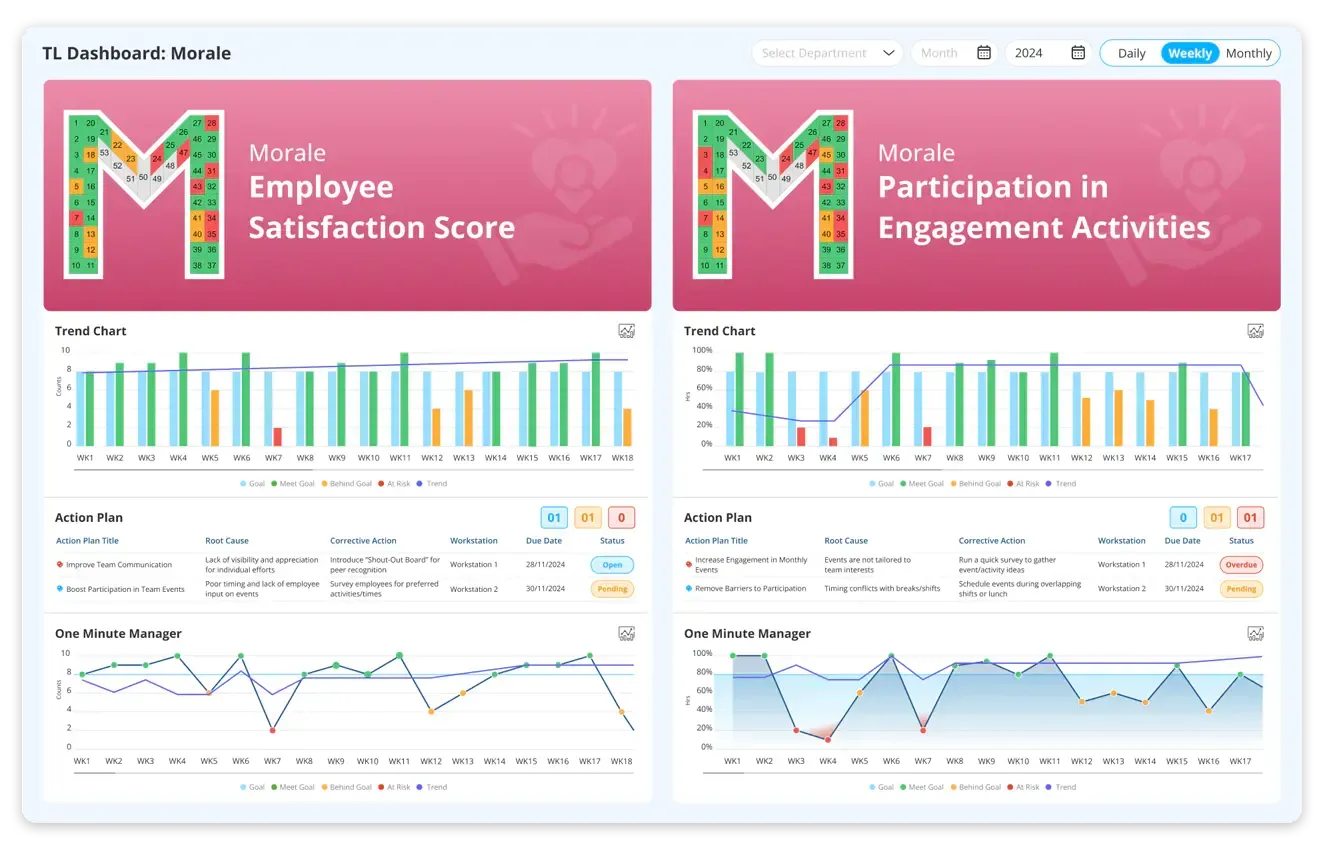
Morale: Morale, as a metric in the SQDCM digital solution, reflects job satisfaction, teamwork, employee retention, and organisational culture. Declines in morale indicators can serve as early warning signs of potential organisational issues, such as leadership challenges, cultural issues, or inadequate support for employee development.
Why are SQDCM Boards important?
SQDCM board is an essential visual management tool in lean manufacturing and other industries. They provide a concise snapshot of performance in critical areas—Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, and Morale—promoting transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement. Through clear visualisation and real-time tracking, SQDCM boards enable teams to identify enhancement areas, make data-driven decisions, and foster a culture of excellence and efficiency.
SQDCM template- what is it and how to use?

An SQDCM board template is a ready-to-use tool for tracking Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, and Morale in one organised view. Instead of creating a board from scratch, this template gives teams a structured layout where they can simply fill in their own metrics, issues, and actions. Using a pre-designed template saves time, ensures consistency, and keeps everyone focused on the right priorities.
A good SQDCM template should include:
- Clear headings for each category (Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, Morale)
- KPIs or targets for each category
- Daily/weekly performance data fields
- Visual indicators (e.g., colour codes for status)
- Notes or comments section for issues and countermeasures
- Responsible person or owner for each action
SQDCM Excel template vs SQDCM Dashboard
Here you get the answer of “what is the difference between SQDCM Excel and SQDCM Dashboard.”
How are SQDCM Boards used in lean manufacturing?
In lean manufacturing, SQDCM boards are crucial visual management tools for tracking and improving performance across Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, and Morale. Teams use SQDCM boards to display key metrics, such as safety incident reports, defect rates, delivery schedules, production costs, and morale indicators. During daily stand-up meetings or huddles, team members review the information on the boards, discuss progress, identify enhancement areas and develop action plans to address issues promptly. SQDCM boards facilitate data-driven decision-making and foster a continuous improvement culture by providing real-time visibility into performance metrics. These boards help teams align their efforts with organisational goals in Lean manufacturing environments.
What data does an SQDCM board display?
A SQDCM board typically displays a range of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) related to Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, and Morale. KPIs under each metric analyses different aspects of operational performance, aiding in decision-making and continuous improvement efforts across various organisational functions or operations.
- Safety metrics examples - Safety Incident Reports, Near-miss Occurrences, and Safety Training Completion Rates.
- Quality metrics examples - Defect rates, Customer Complaints, and Adherence to Quality Standards.
- Delivery metrics examples - On-time Delivery Rates, Lead Times, and Order Fulfilment Status.
- Cost metrics examples - Cost of Raw Materials, Production Costs, Energy Consumption Costs, and Recycling Costs.
- Morale metrics examples - Employee Satisfaction, Survey Results, and Turnover Rates.
Learn How to measure SQDCM for better organisational performance.
How does a SQDCM Board work?
Implementing a digital SQDCM board in an organisation involves several steps to ensure their effectiveness and successful integration into daily production processes:
- Select the right visual management board: Research and select the best visual management solution that aligns with your organisational goals. Look for features such as customisable dashboards, real-time data updates, report generation and user-friendly interfaces.
- Define the metrics and KPIs: Have a proper idea of the arrangement of metrics and other visual elements on your visual management board. For a SQDCM board, the metrics are Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost and Morale. These metrics can be customised to form a SQDCP board, SQDCL board or SQDC board as per your industrial requirements.
- Specify the KPIs tracked under each SQDCP metrics: Choose the Key Performance Indicators to be tracked under each metrics which relates to a specific strategic goal or improvement that your organisation needs to achieve.
- Set the frequency for the SQDCM board: Conduct regular review meetings or huddles where teams analyse the data displayed on the SQDCM board. The frequency set for analysing your SQDCM board solely depends on the size and nature of your industrial operations.
- Update and monitor your SQDCM board: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of SQDCM boards in driving performance improvements and achieving organisational goals. Evaluate the relevance of SQDCM metrics, board template, and communication strategies to make adjustments as needed and ensure alignment with strategic objectives.
- Integrate with relevant platforms: Integrate with the systems for collecting, updating, and reporting data for each KPI on the SQDCM board. SQDCM boards support automation and integration with production management systems, quality systems and maintenance management systems, saving time and preventing data redundancy.
- Analyse the root causes of unattained goals:
How to customise an SQDCM board for your process
The SQDCM board serves as a versatile solution across several industries, including manufacturing, automotive, healthcare, pharmaceuticals, energy, electronics, aviation, marine vessels, banking, service sectors and beyond.
To choose the right SQDCM template for your industry, follow these steps:
- Assess Industry/ Process Requirements: Understand the specific needs, priorities, and challenges of the industries or processes where the SQDCM board will be implemented.
- Select a Visual Management Board and Tailor Metrics to Industry or Process Needs: Customise the selection of metrics to align with the unique characteristics and requirements of the industry or process. When defining metrics, consider safety protocols, quality standards, production lead times, cost structures, and employee morale indicators.
- Design Board Layout and Visual Elements: Design the layout of the SQDCM Board to accommodate industry-specific information and visual elements. Use colour-coded sections and graphs to convey information effectively and enhance visual clarity.
- Incorporate Industry-Specific Best Practices: Research industry-specific best practices and performance improvement methodologies relevant to safety, quality, delivery, cost, and morale. Incorporate elements of lean manufacturing, Six Sigma, Total Quality Management (TQM), or other relevant frameworks into the design of the SQDCM Board.
How do SQDCM Boards contribute to Process Improvement?
SQDCM boards play a pivotal role in driving process improvement by visually representing Key Performance Indicators, fostering accountability, and enabling real-time monitoring of process efficiency. By establishing clear metrics for Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, and Morale, SQDCM boards drive process improvement. A SQDCM board benefits for process enhancement in many ways:
- Identification of improvement areas
- Tracking progress toward goals
- Timely corrective actions
- Regular review and analysis of data
- Identification of trends and root causes of inefficiencies
- Continuous improvement culture fostered
- Enhanced operational performance
- Improved cost efficiency
- Increased employee engagement
Why should you track and measure each metric in a SQDCM Board?
In a SQDCM (Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, Morale) board, tracking and measuring each metric is crucial for several reasons. Each metric on the SQDCM board shows the organisation's performance in key areas essential for operational excellence and continuous improvement. By tracking and measuring these metrics, businesses can set targets, identify trends, and implement corrective actions to enhance overall efficiency, productivity, and employee satisfaction while ensuring alignment with strategic goals.
➤ Safety
- Incidence Rate: Measure the frequency of safety incidents within a defined period.
- Near Misses: Track instances where accidents almost occurred, providing insight into potential hazards.
- Compliance: Ensure adherence to safety regulations and protocols to prevent workplace injuries