Best practices to achieve Zero Defect Manufacturing in Aerospace Industry
August 18, 2025
A chief quality officer at a major aircraft assembly plant reported that over 60% of rework incidents could be traced back to errors in early-stage production checks. This revelation reshaped the company’s entire approach to quality, shifting focus towards prevention rather than correction.
Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) is still highly relevant and continues to gain importance in modern manufacturing. While achieving zero defects in practice can be challenging, it remains a valuable aspirational goal that drives continuous improvement in quality and efficiency.
But how do you eliminate errors in processes involving thousands of components, tight tolerances, and relentless pressure?
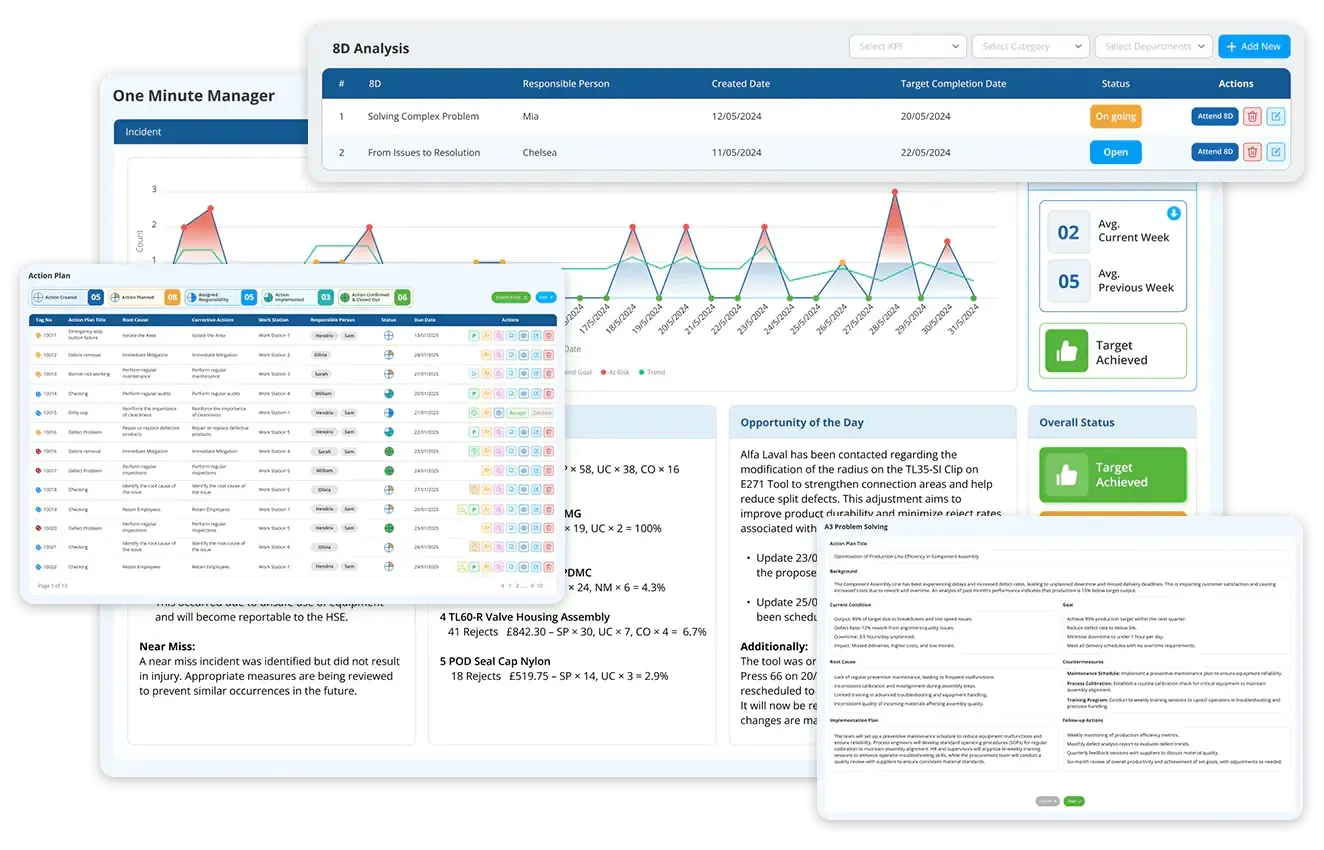
The answer lies in embracing proven methodologies with smart technology. This blog breaks down five actionable best practices to achieve ZDM in Aircraft Parts manufacturing —and reveals how smart digital tools like LTS Data Point Balanced Scorecard turn these principles into measurable, sustainable results.
What is Zero Defect Manufacturing?
Zero Defect Manufacturing is a quality management approach that focuses on eliminating errors at the source rather than correcting them downstream. It shifts the mindset from “inspecting for errors” to “building processes where errors can’t occur.”
Why does Zero-Defect Quality assurance matter in Aerospace Industry?
If you’ve ever wondered why aerospace manufacturers obsess over the tiniest details, it’s because in this industry, there’s no such thing as an “acceptable margin of error.” From aircraft engines to the last rivet on a wing panel, Zero-Defect Quality Assurance is the difference between a flawless flight and a grounded fleet.
Why is it important?
- In