What is the Continuous Improvement Process?
Continuous improvement processes systematically enhance operations, products, or services over time through incremental or breakthrough changes. Continuous improvement involves identifying enhancement areas, implementing changes, measuring outcomes, and repeating the cycle to achieve ongoing progress. The continuous improvement initiatives fosters a culture of innovation, efficiency, and excellence within organisations by encouraging regular reflection, adaptation, and refinement.
In your organisation, you can implement two key types of continuous improvement practices: incremental and breakthrough. It's advisable to combine both approaches to ensure the effectiveness of your continuous improvement processes.
Continuous Improvement principles include:
- Prioritising Customer-centric focus
- Harnessing employees' insights for mutual benefit
- Receiving leadership support
- Implementing incremental changes for sustained progress
- Utilising data-driven methods for informed decision-making.
- Employing continuous improvement software to enhance efficiency.
Five Continuous Improvement Methods for long-term success
There are numerous approaches for implementing continuous improvement initiatives. Here are five of them:
- The Lean Method: Lean focuses on minimising waste and maximising value by streamlining processes and improving efficiency. It emphasises continuous improvement by eliminating non-value-added activities and fostering a problem-solving culture and respect for people.
- The Kanban Method: Kanban is a visual scheduling system that helps teams manage their workflow effectively. It enables teams to visualise work, limit work in progress, and optimise the flow of tasks through the system, promoting continuous improvement and adaptive planning.
- Six Sigma: Six Sigma aims to minimise defects and process variations to achieve consistent quality and customer satisfaction. It relies on statistical analysis and data-driven decision-making to identify and eliminate the root causes of issues.
- Total Quality Management: Total Quality Management (TQM) is an approach to management that aims to improve quality in all aspects of an organisation's operations, products, and services. It involves creating a culture of quality, customer focus, and employee involvement to meet or exceed customer expectations consistently.
- Agile Methodology: Agile is a collaborative and flexible methodology for project management and software development that prioritises adaptability and responsiveness to change. It encourages frequent iterations, adaptive planning, and continuous feedback, promoting continuous improvement and delivering value to customers efficiently.
Why do you need a Continuous Improvement Plan for your business?
A Continuous Improvement Plan (CIP) is important for businesses as it systematically identifies, prioritises, and addresses areas for enhancement within processes, products, and services. By fostering a culture of innovation and adaptability, Continuous Improvement Plan enables businesses to stay competitive in dynamic markets, enhance operational efficiency, and maintain customer satisfaction. Through regular assessment and iteration, Continuous Improvement Plan ensures ongoing optimisation, mitigates risks, and fosters employee engagement and empowerment. Ultimately, a well-executed CIP enables businesses around the globe to drive sustainable growth, improve profitability, and respond to customer needs and market trends.
When should organisations start focusing on Continuous Improvement Processes?
Organisations should prioritise adopting continuous improvement practices, particularly in manufacturing processes, through implementing Kaizen principles from their inception. Embedding these practices early in the organisation can establish a culture of efficiency, innovation, and quality. Emphasising continuous improvement enables companies to swiftly adapt to market demands, minimise waste, and enhance processes for enhanced productivity. Early integration also fosters employee engagement and commitment to ongoing improvement, laying a strong foundation for sustained success and competitiveness in the long term.
How do you promote a culture of Continuous Improvement?
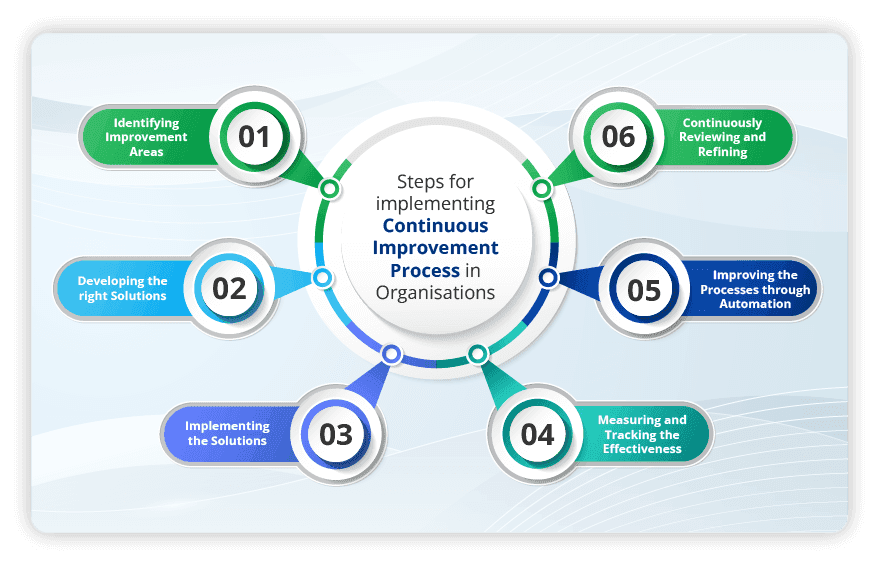
Achieving continuous improvement involves a systematic approach that addresses inefficiencies and drives innovation across all levels of the organisation. The six steps outlined below serve as a roadmap for implementing and sustaining continuous improvement initiatives. By following these steps, businesses can identify opportunities for improvement, develop effective solutions, and improve processes to ensure ongoing success and adaptability in an ever-evolving market. The six steps taken for implementing continuous improvement within organisations include:
- Identifying Improvement Areas: Analysing current shop floor operations enables organisations to pinpoint areas for process improvements and understand the underlying causes of inefficiencies. Performing a Root Cause Analysis (RCA) helps continuous improvement leaders identify areas and procedures that need to be improved.
- Developing the right Solutions: Organisations must brainstorm and devise effective solutions to address specific challenges and objectives once improvement areas are identified. Creating the right solutions contributes to enhancing overall operational procedures within organisations.
- Implementing the Solutions: Implementing proposed solutions involves making necessary adjustments to existing processes, workflows, and systems to facilitate meaningful change and improvement.
- Measuring and Tracking the Effectiveness: Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) allows organisations to measure the impact of implemented solutions and track progress towards desired outcomes over time.
- Improving the Processes through Automation: Embracing automation can streamline operations, reduce manual effort, and enhance consistency, enabling organisations to achieve higher levels of efficiency and productivity.
- Continuously Reviewing and Refining: It is essential to consistently evaluate and adapt to maintain momentum and drive continuous improvements cyclically.
Why is 5S the cornerstone of a successful Continuous Improvement Plan?
The 5S system serves as the cornerstone of a successful continuous improvement plan due to its fundamental principles of sorting, setting in order, systematic cleaning, standardising, and sustaining discipline. By implementing 5S processes, organisations establish a structured framework for organising the workplace, optimising efficiency, and minimising waste. The 5S principles promote a culture of discipline, visual management, and continual improvement, laying the groundwork for further improvement initiatives such as lean manufacturing and Kaizen. Through the systematic application of 5S methodologies, businesses can enhance safety, quality, and productivity while fostering employee engagement and ownership of the improvement processes.
Continuous Improvement Tools and Techniques
Businesses employ continuous improvement strategies, using several tools and techniques to drive organisational growth and efficiency. These methods enable systematic process improvements across shop floor operations, fostering a culture of innovation and adaptability. Here are key tools and techniques utilised in continuous improvement process:
- Balanced Scorecard Software: Balanced Scorecard Software aligns strategic objectives and tracks KPIs across financial, customer, internal processes, and learning & growth perspectives, facilitating continuous improvement in organisations.
- PDCA Cycle: The PDCA cycle enables iterative problem-solving and continuous improvement of processes through planning, execution, evaluation, and adjustment.
- 5S Software: 5S software facilitates implementing and maintaining workplace organisation and standardisation, which is essential for sustaining improvement efforts.
- Hoshin Kanri X Matrix : Hoshin planning and hoshin catchball methodologies align organisational objectives with actionable strategies, ensuring continuous improvement initiatives are driven by clear goals and collaboration.
- Kanban Board: Kanban visualise workflows, promotes task management, and facilitates timely responses to changes, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
- Value Stream Mapping: Value Stream Mapping identifies and eliminates waste in processes, optimising value delivery and enhancing overall performance.
- TIMWOOD: TIMWOOD identifies seven types of waste—transportation, inventory, motion, waiting, overproduction, over-processing, and defects—guiding efforts to minimise inefficiencies.
- Kaizen Events: Kaizen Events facilitate focused improvement initiatives, empowering cross-functional teams to address specific challenges and drive incremental enhancements.
- Root Cause Analysis: Root Cause Analysis identifies underlying factors contributing to problems, enabling targeted solutions and preventing recurrence.
- 5 Whys: The 5 Whys technique delves deep into the root causes of issues, promoting through problem-solving and informed decision-making.
- Gemba Walks: Gemba Walks involve leaders engaging directly with frontline employees to observe processes directly, identify improvement opportunities, and foster collaboration.
- Visual Management Systems: Visual Management Systems enhance communication, transparency, and accountability, ensuring alignment with improvement goals and facilitating continuous monitoring and adjustment.
- Continuous Improvement Software: Continuous improvement software is a digital tool designed to facilitate the ongoing improvement of processes, products, and services within an organisation. Key features include performance tracking, root cause analysis, action planning, and workflow automation.
How do you identify areas of Improvement at work?
Identifying continuous improvement areas is crucial for organisational growth and efficiency. Here's how to pinpoint these opportunities:
- Employee Feedback and Suggestions: Encourage employees to share insights and ideas for improvement based on their firsthand experiences and expertise. Their perspectives can uncover inefficiencies and suggest innovative solutions.
- Process Analysis: Conduct thorough evaluations of existing operational processes to identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and waste areas. Utilise techniques like Value Stream Mapping and Root Cause Analysis to pinpoint improvement opportunities.
- Customer Feedback and Complaints: Actively gather customer feedback regarding their experiences with products or services. It is important to analyse complaints and suggestions to identify patterns and areas for enhancement to meet customer needs and expectations better.
- Benchmarking: Compare organisational performance against industry standards and best practices. Benchmarking highlights areas where the organisation falls short and identifies opportunities for improvement to enhance competitiveness.
- Performance Metrics and Data Analysis: Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and analyse data to identify trends, anomalies, and areas of underperformance. Data-driven insights provide valuable guidance for targeted improvement efforts.
- Regular reviews and Audits: Conduct regular reviews and audits of processes, systems, and procedures to identify gaps, compliance issues, and opportunities for streamlining or automation.
- Market research and Environmental scanning: Stay informed about market trends, technological advancements, and regulatory changes. Proactively anticipate challenges and opportunities to adapt and improve organisational practices.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: Foster collaboration and communication across departments and teams to leverage diverse perspectives and expertise. Cross-functional teams can identify and address improvement opportunities holistically.
How do you track Continuous Improvement activities?
Continuous Improvement activities can be tracked through various visual metrics dashboards like a Balanced Scorecard. Tracking your continuous improvement initiatives helps with regular performance reviews. Organisations employ data analytics tools and software systems to monitor progress, identify trends, and measure the impact of improvement initiatives. Feedback mechanisms, employee surveys, and suggestion systems also facilitate ongoing evaluation and refinement of improvement processes. Continuous Improvement tracking involves setting clear objectives, establishing measurable targets, and regularly reviewing performance against predefined benchmarks and continuous improvement metrics. By leveraging these approaches, organisations can effectively monitor their improvement efforts, identify areas for optimisation, and drive sustainable growth and innovation.
Benefits of Continuous Improvement in the workplace
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlining processes and reducing waste enhances productivity and resource utilisation.
- Quality Improvement: Continuous improvement fosters a culture of excellence, leading to higher-quality products and services.
- Cost Reduction: Identifying and eliminating inefficiencies lowers operational costs and improves profitability.
- Greater Employee Engagement: Involving employees in improvement initiatives boost morale, motivation, and job satisfaction.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Delivering consistent quality and value meets customer expectations and builds loyalty.
- Innovation and Adaptability: Embracing change and innovation enables organisations to stay competitive and responsive to market demands.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying and addressing problems early minimises risks and prevents costly errors or setbacks.
- Long-Term Sustainability: Continuous improvement ensures organisations remain agile and resilient in evolving business environments.
Who is responsible for Continuous Improvement in an organisation?
In an industrial setting, the responsibility for continuous improvement processes typically extends across various levels of the organisation. While senior leadership sets the tone and provides strategic direction, middle managers play a crucial role in implementing improvement initiatives at the operational level. Frontline supervisors and employees directly involved in production processes are also essential contributors, as they possess valuable insights into daily operations and can identify improvement opportunities firsthand. A culture of continuous improvement thrives when all stakeholders are actively engaged, share accountability, and collaborate to drive innovation and efficiency throughout the organisation. Therefore, in industries, the responsibility for continuous improvement is distributed across leadership, management, and frontline personnel alike.
