Last updated on : January 7, 2026
What is Strategic Planning?
Strategic planning in business is a systematic process that involves setting goals, outlining strategies, and making decisions to achieve long-term success. Strategic Planning is important for businesses because it provides a roadmap for growth, ensuring that companies remain adaptable and competitive in a constantly changing market landscape.
The purpose of strategic planning is to align organisational objectives with available resources, enabling efficient resource utilisation and personnel. The 4 P’s of strategic planning, namely Perceptions, Process, Purpose and Performance, guide businesses in defining their mission, understanding their market position, devising effective plans, and recognising patterns in consumer behaviour for informed decision-making.
➤ Key Elements or Components of the Strategic Plan include:
- A Mission Statement
- A Vision Statement
- Core values
- Goals and Objectives
- Strategies and Operational Tactics
- Action plans
➤ Benefits of having a good Strategic Plan:
- Aligns organisational efforts and resources towards common goals.
- Enhances decision-making by providing a clear roadmap.
- Improves resource allocation and utilisation.
- Facilitates proactive adaptation to changing market conditions.
- Increases organisational focus and accountability.
Strategy Vs Tactics
Strategy and tactics are interrelated concepts in achieving goals, yet they serve distinct roles in planning and execution. A strategy outlines the direction and scope of an organisation's efforts to achieve long-term objectives with its four pillars: Vision, Analysis, Target and Plan. It involves analysing the competitive landscape, identifying opportunities, and aligning resources to achieve sustainable outcomes.
On the other hand, tactics are the specific actions employed to execute the strategy effectively. They are the practical steps taken in the short term to support the strategic plan, addressing immediate challenges and opportunities. While strategy focuses on the big picture and long-term goals, tactics concentrate on the detailed actions and decisions made in the present to realise strategic objectives, ensuring that the overall strategy is implemented successfully.
How often is Strategic Planning done?
Strategic planning is essentially the compass that steers businesses towards their True North, ensuring relevance and resilience in a competitive business environment. The frequency of strategic planning varies depending on an organisation's growth and the industry's dynamics. Typically, businesses aim to create a comprehensive strategic plan every three to five years to align their objectives with the evolving market demands and internal capabilities. However, a biennial review is necessary for faster-paced organisations to ensure their strategies remain flexible and relevant. Small businesses may find the need for more frequent updates, perhaps on an annual basis, to reflect their agility in responding to changing market trends and customer demands.
By conducting regular assessments and adjustments, businesses can sustain their competitiveness and adapt to evolving business landscapes effectively. It is crucial to apply these strategic plans not only in day-to-day operations but also in long-term decision-making, resource allocation, and performance evaluation. This holistic approach ensures that the strategic planning process becomes an ongoing, integral part of the business, enabling it to navigate the challenges of the ever-changing business environment successfully.
How to write a Strategic Plan for a business?
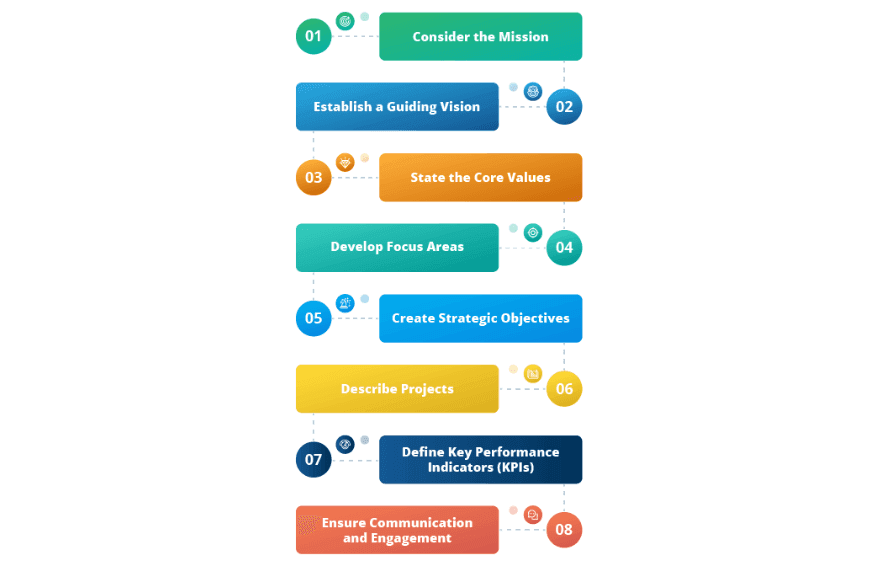
Creating a strategic plan is crucial for guiding an organisation towards its goals.
Consider the Mission
Define the organisation's purpose. "What does your organisation aim to achieve?" , "Who does it serve?" The mission statement should clearly convey the core purpose of the organisation.
Establish a Guiding Vision
Create a compelling vision statement that describes the desired future state of the organisation. It should inspire and motivate all stakeholders. The vision statement outlines what the organisation aspires to become.
State the Core Values
Identify the core values that guide the organisation's culture and decision-making. Core values represent the organisation's beliefs and principles. They serve as a moral compass for everyone involved.
Develop Focus Areas
Identify key focus areas or strategic themes. These are broad areas of focus that align with the mission and vision. They provide a framework for the strategic objectives and initiatives that will follow.
Create Strategic Objectives
Define clear, Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) strategic objectives for each focus area. Strategic objectives outline the desired outcomes and set the direction for the organisation. Each objective should contribute to the overall vision.
Describe Projects
Identify specific projects or initiatives that will help achieve each strategic objective. Projects are actionable tasks or programs designed to fulfil strategic objectives. Describe the scope, timeline, resources, and responsibilities for each project.
Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Establish KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) for each strategic objective and project. KPIs are quantifiable measures that indicate progress toward achieving objectives. They help track performance and determine whether the organisation is moving in the right direction.
Cascade the Strategy
Cascading strategy ensures alignment by translating overarching goals into specific, actionable objectives at different levels of the organisation. It fosters clarity, coordination, and unified focus, enhancing teamwork resource efficiency and maximising the organisation's ability to achieve strategic goals.
Stages of a Strategic Management Process
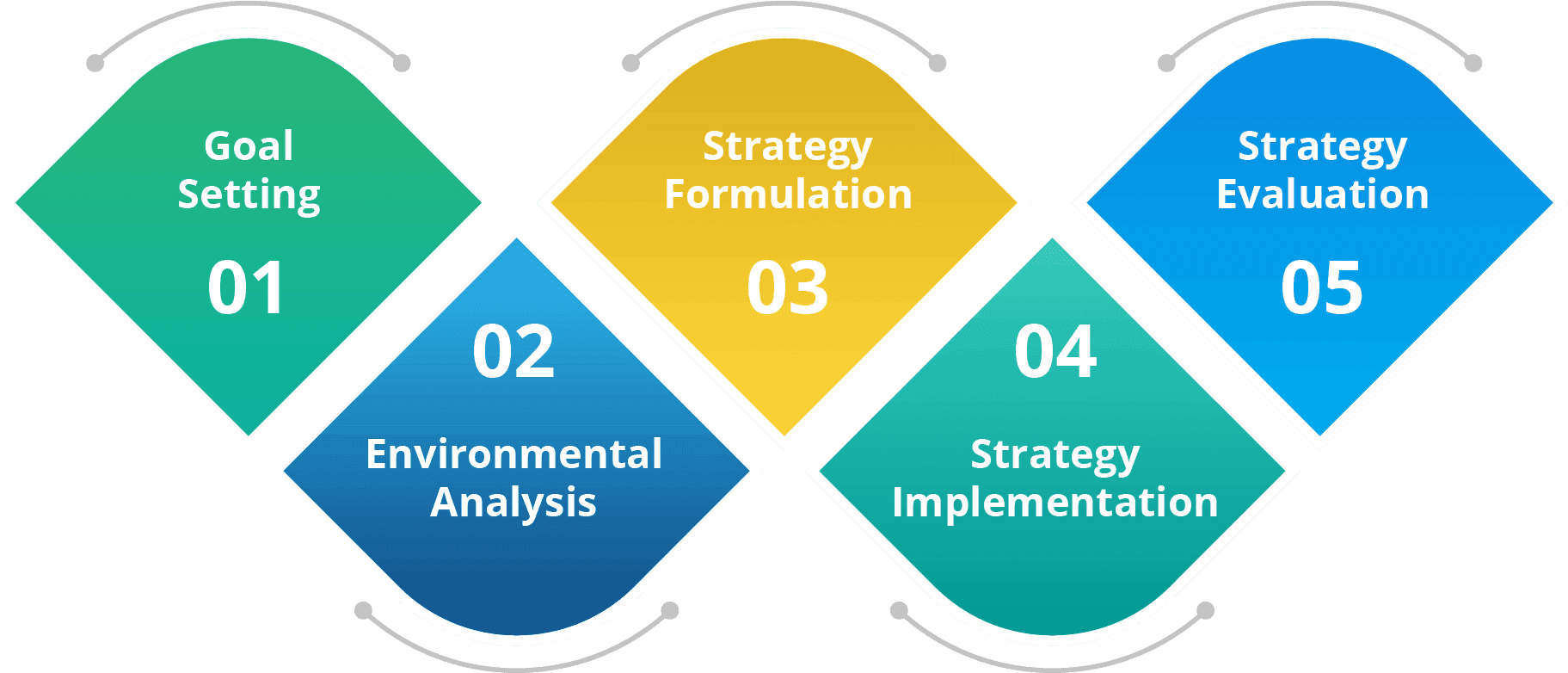
Strategic management is an all-encompassing process that involves formulating, implementing, and evaluating goals and strategies to accomplish an organisation's objectives. Strategic management aims to make informed decisions and create action plans that shape and guide an organisation's processes to achieve its objectives efficiently and effectively. If you want to build and structure your strategic plan, here's how to do it:
- Goal Setting: At the onset of the strategic management process, organisations engage in goal setting, where clear strategic objectives and goals are defined. Establishing objectives that adhere to the principles of Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART goals) is crucial. Goal setting provides a clear direction for the organisation and helps in aligning the efforts of employees towards achieving common objectives.
- Environmental Analysis: A detailed analysis of the organisational environment involves assessing and understanding the external and internal factors that can affect the organisation's performance. Environmental analysis helps to identify opportunities and threats, enabling the organisation to make informed strategic decisions. SWOT analysis, PEST analysis and Ansoff matrix can be effectively used during this stage.
- Strategy Formulation: The organisation develops strategies based on the goals set and the analysis of the internal and external environment. Strategies can be of different types, such as corporate, business, or functional strategies. Corporate strategy deals with the overall scope and direction of the organisation. Business strategy focuses on how a particular business unit or product line will compete in the market. Functional strategies pertain to specific organisational functions, such as operations or marketing. The chosen strategies should align with the organisation's mission, vision, and overall objectives.
- Strategy Implementation: Once the strategies are formulated, they need to be translated into action plans. The strategic implementation involves allocating resources, defining tasks and responsibilities, creating a supportive organisational structure, and ensuring that the necessary processes and systems are in place to execute the strategies effectively.
What is a Strategy Map?
The strategy map is a visual tool that illustrates an organisation's strategic objectives and their interconnections. It offers a clear overview of the company's mission, vision, and key goals, demonstrating the relationships between different objectives. Strategic objectives, encompassing Financial, Customer, Internal processes, and Learning & Growth perspectives (FCIL), are interconnected to show how improvements in one area impact another, aligning with the overall mission. The Balanced Scorecard is a holistic strategic management tool that translates objectives into specific performance measures across FCIL perspectives. These measures can be integrated to create a strategy map in the Balanced Scorecard to provide a comprehensive view of the organisation's strategy, enhancing communication, execution, and monitoring of strategic initiatives.
Tools and frameworks for Strategic Planning, Management and Execution
- Balanced Scorecard (BSC): The Balanced Scorecard translates strategic objectives into Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning & Growth (FCIL) perspectives, ensuring a balanced approach to performance measurement and strategy execution.
- Strategy Map: A Strategy Map visually represents an organisation's strategic objectives and their cause-and-effect relationships, enhancing understanding and communication of the overall strategy.
- Quad Charts: Quad Charts condense complex information into four quadrants, aiding in concise communication of project status, risks, and future plans, enabling efficient strategic planning and decision-making
- SWOT Analysis: SWOT analysis evaluates an organisation's Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, helping in strategic decision-making by identifying internal capabilities and external factors affecting the business.
- PEST Analysis: PEST analysis assesses Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors impacting a business, providing insights into the external macro-environment, aiding strategic planning and risk management.
- VRIO Framework: The VRIO framework assesses a firm's internal strengths and weaknesses by evaluating the Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organisation of its resources and guides strategic resource allocation.
- Porter's Five Forces: Porter's Five Forces model analyses the level of competition within an industry based on factors such as the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, along with the threat of new entrants and competitive rivalry. It helps with strategic decision-making.
Using Balanced Scorecard for Strategic Alignment
Balanced Scorecard software plays a crucial role in aligning organisational goals and objectives by providing a centralised platform to define, track, and communicate strategic goals and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Through this software, businesses can systematically cascade their strategic goals and objectives from the top management level to every department and employee. It enables the clear articulation of strategic objectives, allowing businesses to break them down into actionable tasks and align action plans with the organisational goals effectively. By visualising the progress of these objectives and KPIs in real-time, businesses can monitor performance at various levels, ensuring that every action taken resonates with the overarching strategic direction. This alignment ensures that employees at all levels understand their roles in achieving the company's strategic vision, promoting a focused approach throughout the organisation.
What are the Key Features to look for when choosing a Balanced Scorecard software for Strategic Management?
When choosing a Balanced Scorecard software for strategic management, consider the following key features to ensure it meets your organisation's needs.
- User-Friendly Interface: Look for a Balanced Scorecard solution with an easy-to-navigate and user-friendly interface, ensuring broad adoption across the organisation.
- Customisability: The software should allow you to customise scorecards, KPIs, and reports to align with your organisation's specific goals and metrics.
- Integration Capabilities: Choose a Balanced Scorecard software that integrates seamlessly with other tools and systems your organisation uses, such as CRM or ERP software, ensuring data consistency and accuracy.
- Real-Time Updates: The ability to provide real-time updates and data visualisation is crucial for monitoring progress and making timely strategic decisions.
