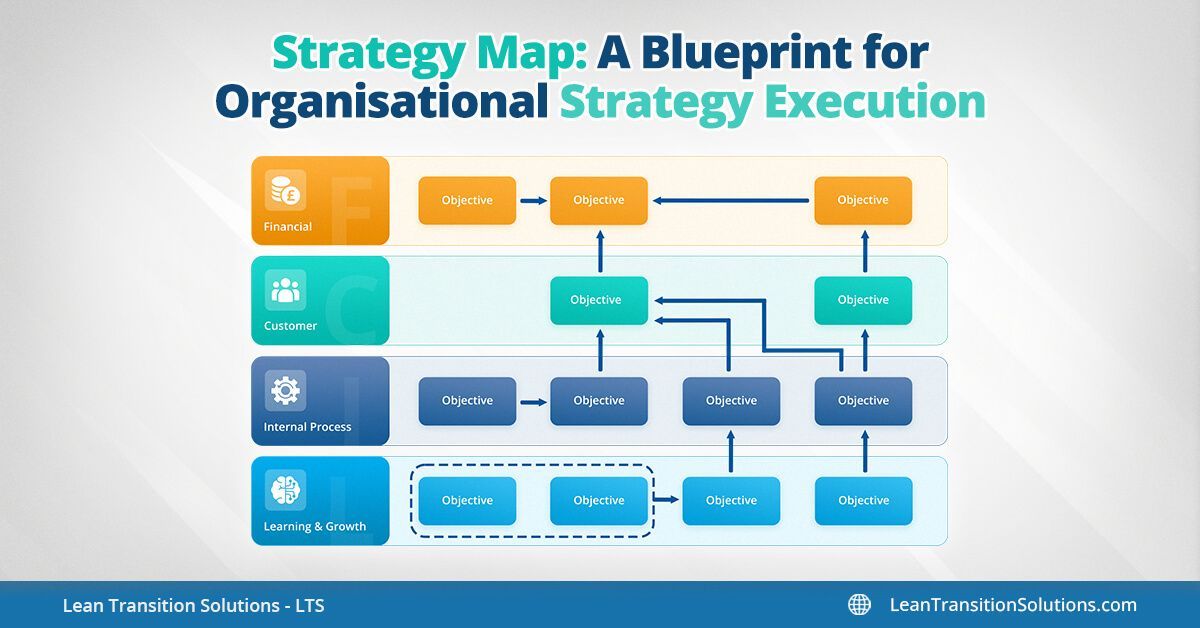
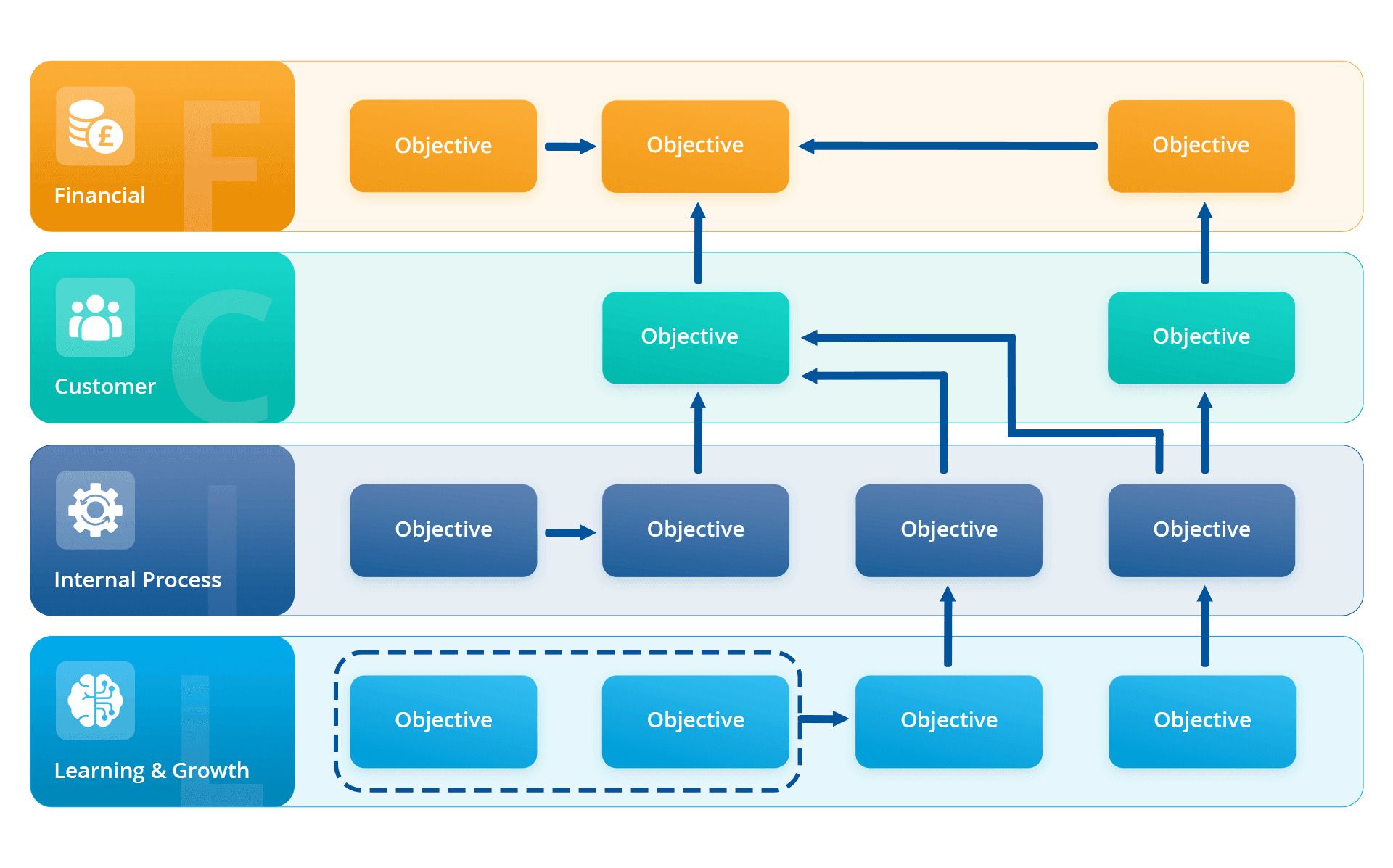
Balanced scorecard strategy map examples
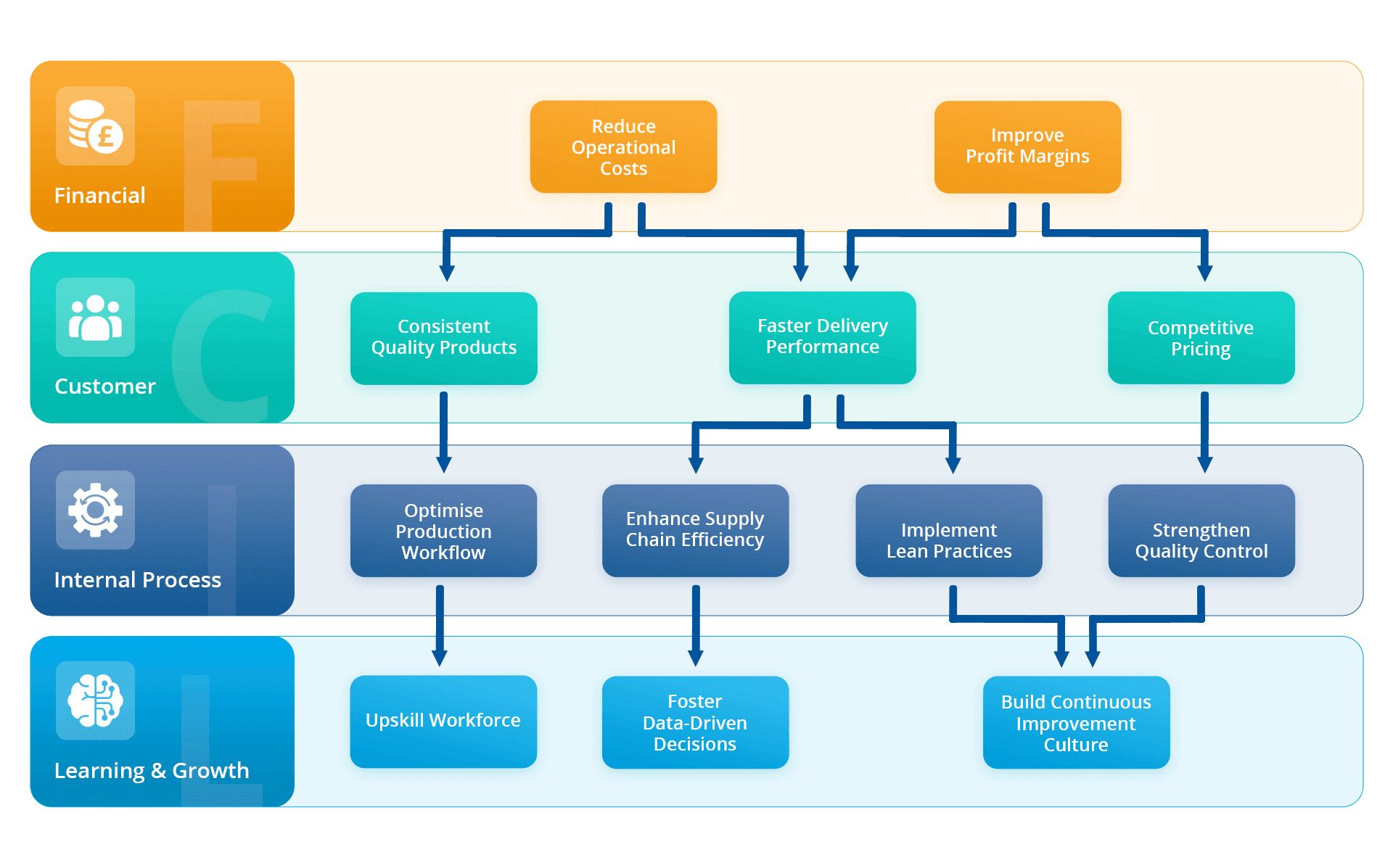
Manufacturing industry
In manufacturing, visual clarity in a strategy map helps spot production bottlenecks, streamline planning, optimise resource allocation, boost productivity, and cut costs. Along with that strategy map helps manufacturing teams aligns their overall actions in a single graphic map.
For example, reducing the cost per unit is supported by improving product quality and delivery time, minimising rework, and training teams in lean practices like continuous improvement and daily lean management.
Healthcare industry
In healthcare, strategy maps improve and help leaders with visual clarity to connect patient care goals with operational priorities. Its visual features—whether digital dashboards or physical charts—make it easier to identify bottlenecks in care delivery, track compliance, and align staff efforts. This clarity helps hospitals and clinics plan resources effectively, improve treatment outcomes, and meet both patient and regulatory expectations.
For patients, this visual map helps hospitals to reduce wait times, standardise treatments, and improve staff coordination—leading to safer care, faster recovery, and better overall experiences.
Banking sector
Strategy map provides the banking sector with clear visual clarity in both planning and execution. By aligning objectives across four perspectives, banks can easily see how different activities connect.
For example, from a financial perspective, banks focus on improving profitability through cost control and balanced lending. The customer perspective emphasises building trust and loyalty with better digital experiences and personalised services. The internal process perspective ensures efficiency by streamlining loan approvals, enhancing compliance checks, and reducing delays. Finally, the learning & growth perspective highlights the need to upskill employees in fintech tools and data-driven decision-making.
This visual flow makes it easier for banking leaders to communicate strategy, align departments, and track progress, ensuring that every initiative contributes directly to stronger customer relationships and improved financial performance.
Data Point – The best software to map your strategy
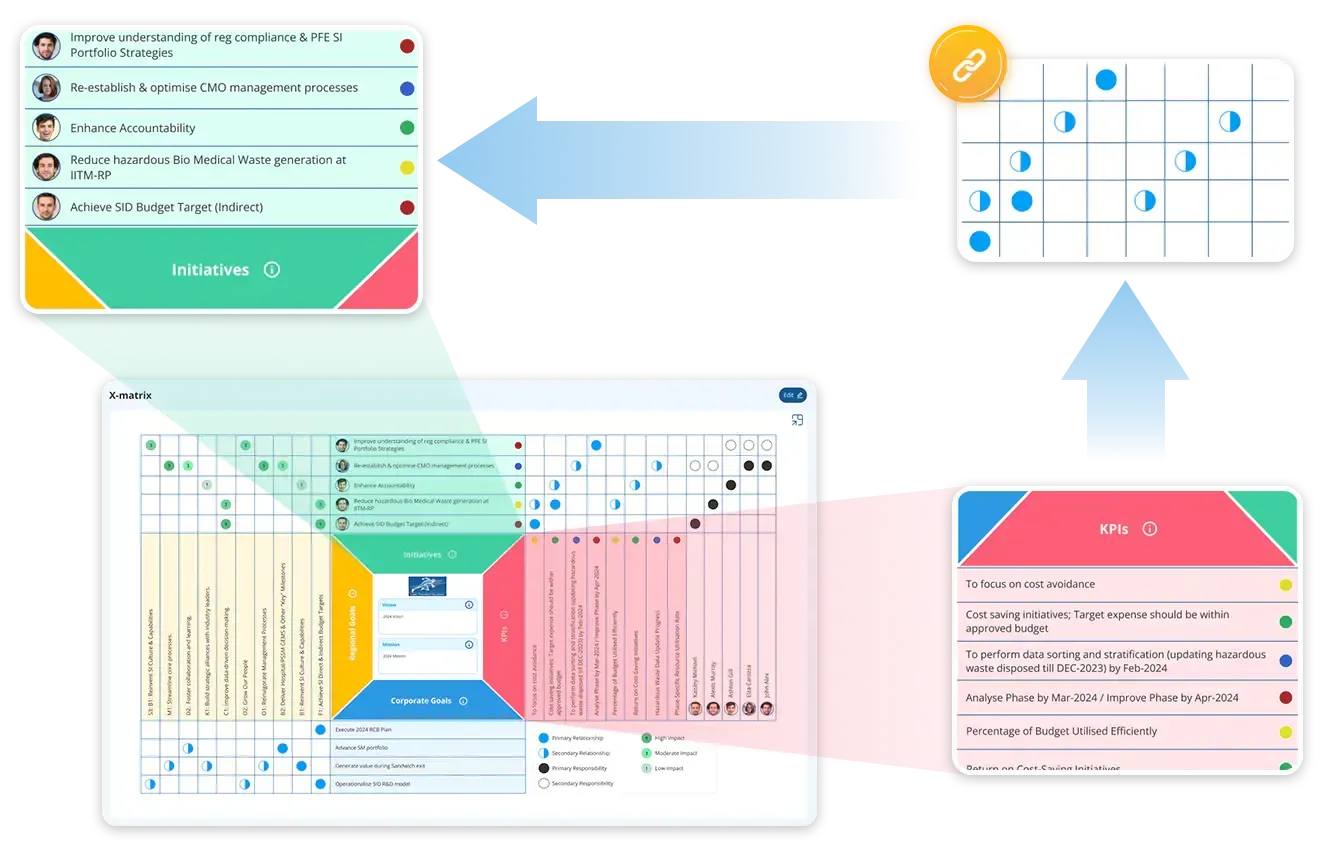
LTS Data Point is more than just a strategy map tool—it’s a comprehensive operational excellence platform designed to visually connect strategic goals, KPIs, and daily actions. As the best strategy map and planning software for manufacturing and lean-driven industries, Data Point empowers leaders to map their vision, align teams, and track real-time insights and optimise performance with unmatched clarity.
With interactive mind maps and x-matrix integration, managers can link SMART goals, KPIs, OKRs, and key focus areas of FCIL. The software seamlessly incorporates SWOT and gap analysis template, making it ideal for robust strategic planning. Data Point creates a visual strategy map that transforms abstract objectives into actionable plans using intuitive drag-and-drop functionality and color-coded goal tracking.
Key features include:
- Visual representation of goals, KPIs, OKRs, and strategic priorities
- Multi-user access across departments for collaborative planning
- Real-time KPI tracking with WIP dashboard, OEE (overall equipment efficiency) dashboard, Super dashboard, Scorecard dashboard
- Integrated daily digital huddle tools for frontline strategic alignment
- Team leader dashboard and one minute manager for quick status reviews
- Daily lean management boards for SQDCP frameworks, SQDCM templates for continuous improvement
- Seamless linkage with Hoshin Kanri X-matrix for top-down strategy execution
- Performance dashboards to monitor departmental, individual, and cross-functional performance
LTS Data Point provides a complete strategy to execution mapping. From high-level goal mapping to on-the-ground performance tracking, it ensures your entire organisation is moving in one direction—towards operational excellence. This makes Data Point -the best software for strategy mapping.
Benefits of using a strategy map
- Strategic alignment across teams- strategy maps visually connect company-wide objectives with departmental and individual goals, ensuring everyone works toward the same mission.
- Enhanced decision-making- with clear root cause analysis techniques, managers can better prioritise resources and choose actions that drive measurable results.
- Improved communication- strategy maps simplify complex goals, making them easier to communicate across leadership, shop floor teams, and support functions.
- Performance visibility- when combined with KPIs and dashboards, strategy maps help track progress in real time and identify gaps before they escalate.
- Supports continuous improvement- strategy maps integrate well with lean tools like PDCA and Hoshin Kanri matrix, reinforcing a culture of ongoing performance improvement.
- Cascade goals and streamline execution- it turns strategic planning into actionable steps by clearly defining goals across financial, customer, process, and learning perspectives.
- Drives accountability, transparency and traceability- by linking strategic objectives to individual and team responsibilities, ensuring ownership and accountability at every level.
Close the gap between planning and performance – Visualise your strategy now!