What is manufacturing process flow and how to digitise it right?
August 25, 2025
Ever walked through a factory and felt like everything was moving in perfect rhythm—materials coming in, machines humming, teams in sync, and finished goods rolling out seamlessly? That’s not luck. It’s the result of a well-designed manufacturing process flow—the invisible architecture that drives every action on the shop floor.
In this blog, we explore the concept of manufacturing process flow, understand how it's different from general process flows or production workflows, and show you how to visualise, map, and optimise it using digital process flow tools.
What is process flow in manufacturing?
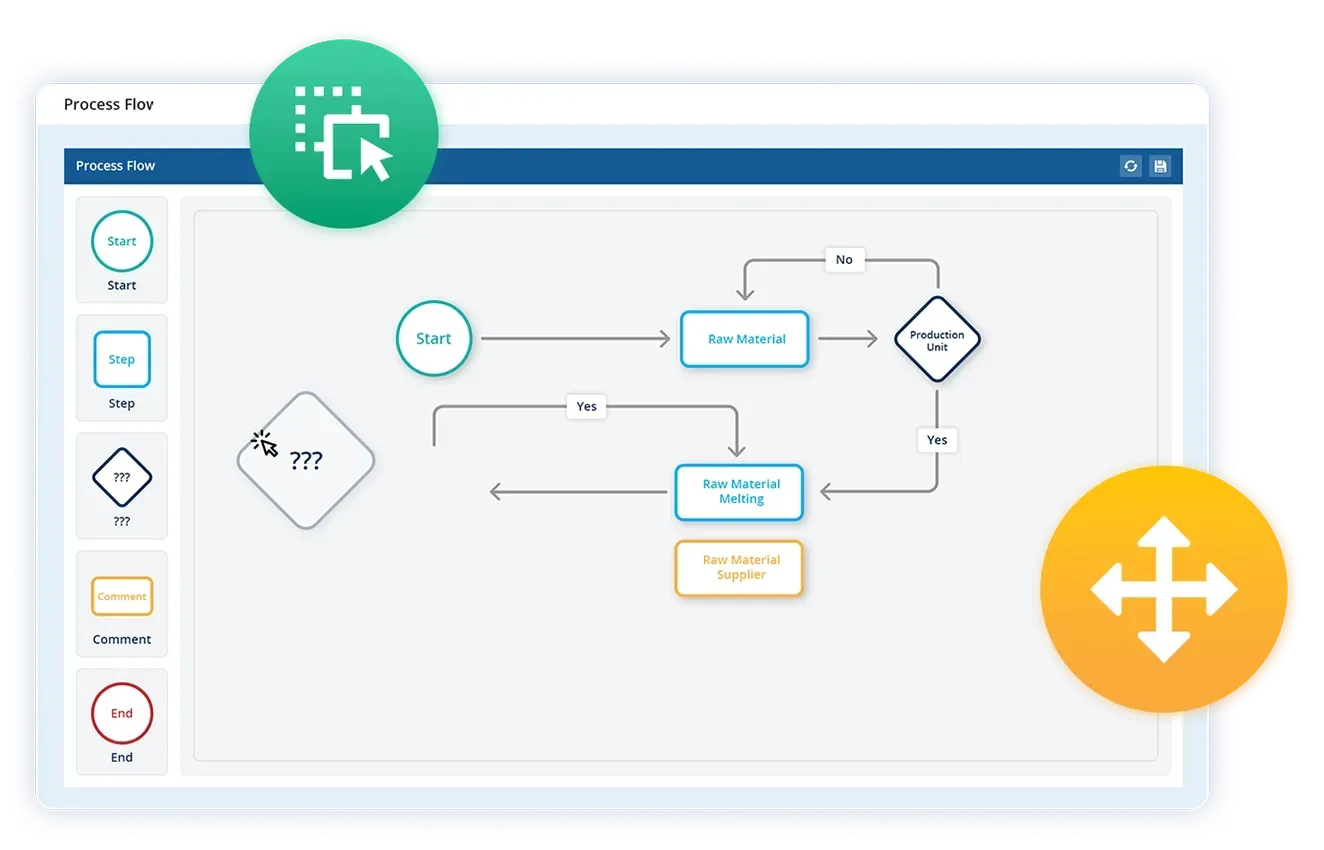
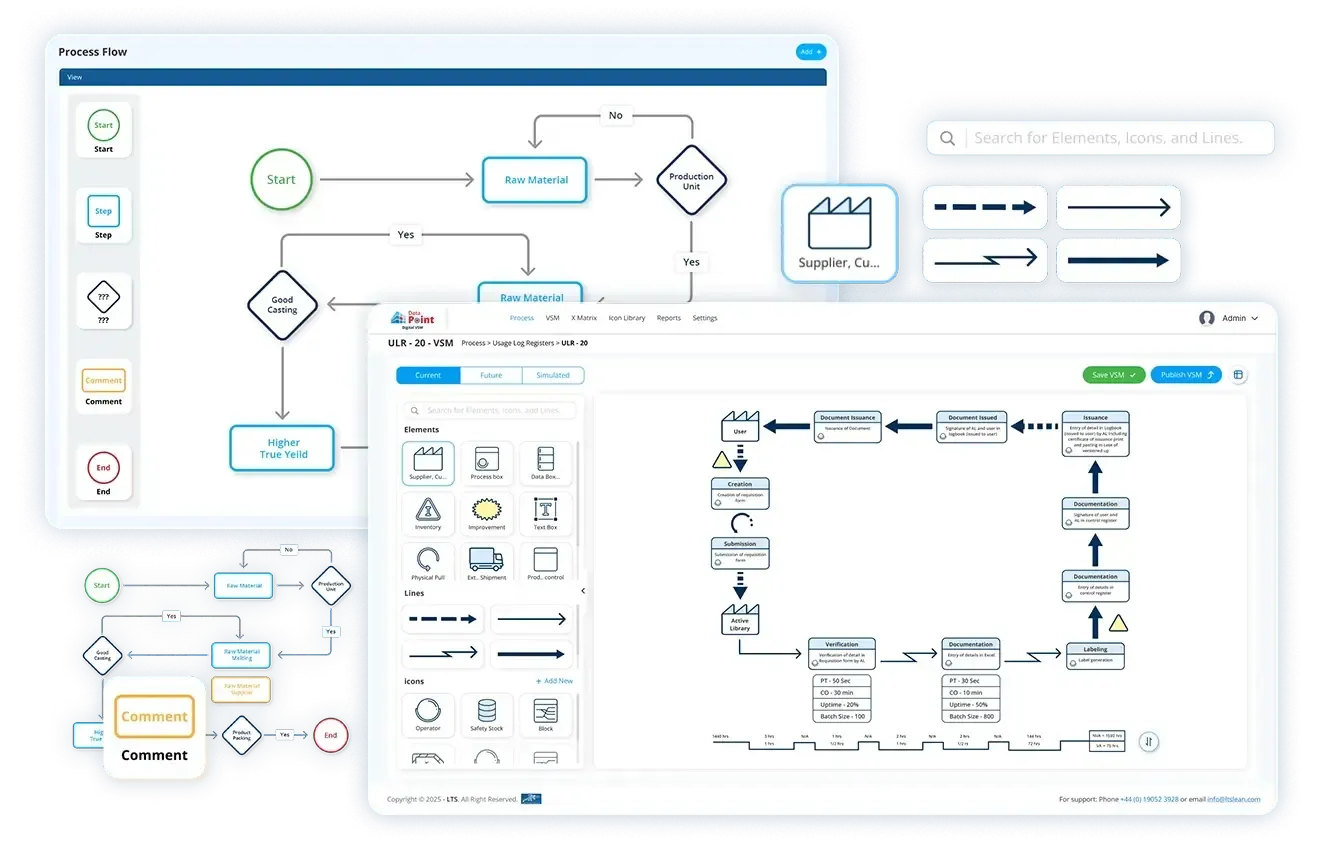
A manufacturing process flow is structured steps in sequential order that outlines how raw materials are transformed into finished products of value. It visually represents the operational flow and production process, from sourcing inputs, moving through machines and workstations, to final packaging and dispatch using- shapes, symbols, and arrows to show the order of operations.
Think of it as a roadmap for your production line, showing every step, decision point, and handoff in the manufacturing journey. It is typically illustrated through process flow diagrams, objective flowcharts, or workflow mapping tools with simple symbols and arrows making it easier to analyse inefficiencies, standardise operations (SOPs), and drive continuous improvement.
Process flow creates a bigger picture of the entire process along with explaining the relationship between each step, leading to process optimisation